-
Table of Contents
«Transforma tu piel con Erythropoietin: descubre una apariencia más radiante y saludable»
Introduction
Erythropoietin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the body to stimulate the production of red blood cells. However, it is also used as a medication to treat certain medical conditions, such as anemia. While Erythropoietin can be beneficial for these purposes, it can also cause changes in the skin. In this article, we will discuss the potential changes that may occur in the skin during the use of Erythropoietin.
Changes in Skin Texture and Elasticity
Erythropoietin, also known as EPO, is a hormone produced by the kidneys that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells. It is commonly used in the treatment of anemia, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease. However, like any medication, EPO can have side effects, and one of the most noticeable ones is changes in skin texture and elasticity.
When a patient starts using EPO, they may notice changes in their skin texture and elasticity. These changes can be subtle at first, but over time, they can become more noticeable. This is because EPO stimulates the production of red blood cells, which in turn increases the oxygen supply to the skin. While this can have positive effects on the skin, it can also lead to some changes that patients should be aware of.
One of the most common changes in skin texture during EPO treatment is dryness. This is due to the increased oxygen supply to the skin, which can cause it to become dehydrated. Patients may notice their skin feeling tight and rough, and in some cases, they may experience flaking or peeling. To combat this, it is important for patients to keep their skin well moisturized. Using a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer can help to alleviate dryness and keep the skin hydrated.
Another change that patients may observe is an increase in oil production. This is because EPO can stimulate the sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oil. As a result, patients may notice their skin becoming more oily and prone to breakouts. To manage this, it is important to maintain a good skincare routine, including cleansing the skin twice a day and using non-comedogenic products. Patients should also avoid using harsh or abrasive products, as these can further irritate the skin.
In addition to changes in texture, patients may also notice changes in skin elasticity. EPO can cause the skin to become thinner and more fragile, making it more prone to bruising and tearing. This is because the hormone can affect the production of collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity. Patients may also notice that their skin becomes more sensitive to the sun, as it is thinner and has less protection against UV rays.
To protect their skin, patients should avoid prolonged sun exposure and always wear sunscreen with a high SPF. They should also be careful when handling sharp objects or participating in activities that may cause friction or pressure on the skin. If a patient does experience bruising or tearing, they should seek medical attention immediately to prevent further damage.
It is also important for patients to be aware of any changes in skin color during EPO treatment. In some cases, the skin may become paler due to the increased oxygen supply. However, in rare cases, patients may experience a condition called erythema multiforme, which causes red or purple patches on the skin. If a patient notices any unusual changes in skin color, they should consult their doctor for further evaluation.
In conclusion, while EPO can be a life-saving medication for patients with anemia, it is important to be aware of the potential changes in skin texture and elasticity that may occur during treatment. By maintaining a good skincare routine and being mindful of any changes in the skin, patients can minimize the impact of these side effects. It is also crucial for patients to communicate with their doctor if they experience any concerning changes in their skin, as prompt medical attention can help to prevent further complications. With proper care and monitoring, patients can manage these changes and continue to benefit from the positive effects of EPO on their overall health.
Appearance of Bruising or Discoloration
Erythropoietin, also known as EPO, is a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates the production of red blood cells. It is commonly used in the treatment of anemia, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease. However, like any medication, EPO can have side effects, including changes in the appearance of the skin. In this article, we will discuss the changes that may occur in the skin during the use of Erythropoietin, specifically the appearance of bruising or discoloration.
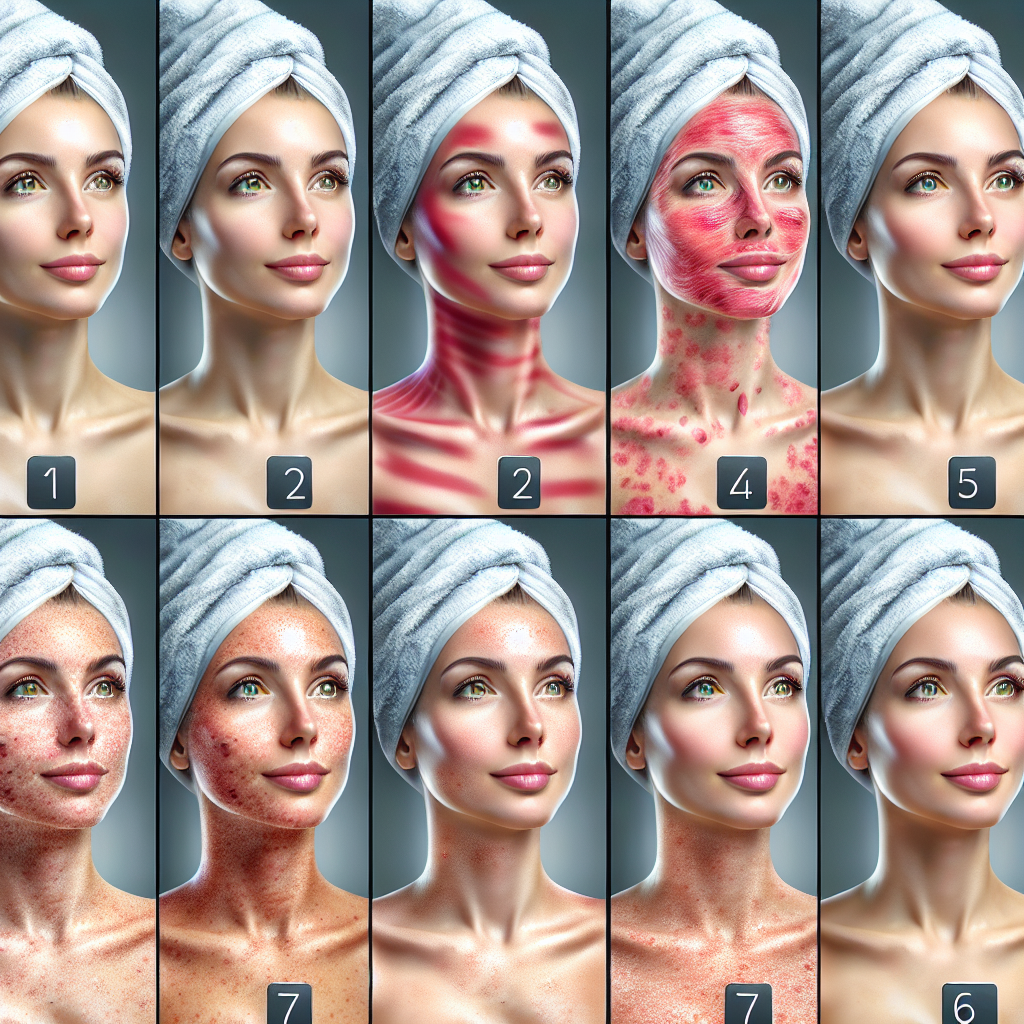
One of the most common side effects of Erythropoietin is the development of bruising or discoloration on the skin. This can be a result of the medication’s effect on the body’s blood clotting mechanism. EPO stimulates the production of red blood cells, which in turn increases the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets are responsible for blood clotting, and an increase in their number can lead to easier bruising and discoloration.
Bruising is the result of blood leaking from damaged blood vessels into the surrounding tissue. It appears as a purple or blue mark on the skin and can be tender to touch. Bruises can occur anywhere on the body, but they are more common in areas with thinner skin, such as the arms and legs. During the use of Erythropoietin, patients may notice an increase in the frequency and severity of bruising.
In addition to bruising, discoloration of the skin may also occur. This can manifest as a darkening or reddening of the skin, particularly in areas where there is increased blood flow, such as the face and neck. This discoloration is often temporary and will fade once the medication is discontinued. However, in some cases, it may persist even after the treatment has ended.
It is essential to note that not all patients will experience bruising or discoloration while taking Erythropoietin. Factors such as age, dosage, and underlying medical conditions can influence the likelihood and severity of these side effects. It is crucial to discuss any concerns with your doctor, who can monitor your skin’s appearance and adjust your treatment if necessary.
If you do experience bruising or discoloration while taking Erythropoietin, there are some steps you can take to manage these side effects. Firstly, it is essential to avoid any activities that may increase the risk of bruising, such as contact sports or heavy lifting. Secondly, you can apply a cold compress to the affected area to reduce swelling and pain. Finally, it is crucial to keep the area clean and dry to prevent infection.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend a topical cream or ointment to help reduce bruising and discoloration. These products can help to improve the appearance of the skin and reduce any discomfort. However, it is essential to consult with your doctor before using any over-the-counter products, as they may interact with your medication.
In conclusion, the use of Erythropoietin can lead to changes in the appearance of the skin, specifically bruising and discoloration. These side effects are a result of the medication’s effect on the body’s blood clotting mechanism and are more common in areas with thinner skin. While not all patients will experience these side effects, it is essential to discuss any concerns with your doctor. They can monitor your skin’s appearance and provide guidance on managing these side effects. With proper care and communication with your healthcare team, you can minimize the impact of these changes on your skin and continue to benefit from the use of Erythropoietin in your treatment.
Increased Sensitivity to Sun Exposure
Erythropoietin, also known as EPO, is a hormone that is naturally produced by the kidneys and is responsible for stimulating the production of red blood cells. It is commonly used as a medication to treat anemia, a condition in which the body does not have enough red blood cells. However, EPO has also been found to have other effects on the body, including changes in the skin. In this article, we will discuss the increased sensitivity to sun exposure that can occur during the use of Erythropoietin.
One of the most common changes observed in the skin during the use of Erythropoietin is an increased sensitivity to sun exposure. This means that the skin becomes more prone to sunburns and other forms of sun damage. This is due to the fact that EPO stimulates the production of red blood cells, which in turn increases the amount of oxygen in the blood. While this is beneficial for the body, it also makes the skin more sensitive to UV radiation from the sun.
UV radiation is a form of energy that is emitted by the sun and can cause damage to the skin. When the skin is exposed to UV radiation, it can lead to sunburns, premature aging, and even skin cancer. Normally, the skin has a natural defense mechanism against UV radiation, in the form of melanin. Melanin is a pigment that gives the skin its color and also helps to protect it from the harmful effects of the sun. However, during the use of Erythropoietin, the increased production of red blood cells can interfere with the production of melanin, making the skin more vulnerable to UV radiation.
In addition to increased sensitivity to sun exposure, Erythropoietin can also cause changes in the skin’s appearance. Some users have reported a darkening of the skin, especially in areas that are exposed to the sun. This is due to the increased production of red blood cells, which can cause an increase in the amount of melanin in the skin. This change in skin color is usually temporary and will fade once the use of Erythropoietin is discontinued.
Another change that can occur in the skin during the use of Erythropoietin is the development of rashes or hives. This is a less common side effect, but it can occur in some individuals. The exact cause of these skin reactions is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the increased sensitivity to sun exposure. If you experience any skin reactions while using Erythropoietin, it is important to consult with your doctor.
To minimize the risk of sun damage and other skin changes during the use of Erythropoietin, it is important to take precautions when going out in the sun. This includes wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, and using sunscreen with a high SPF. It is also recommended to avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially during peak hours when the sun’s rays are strongest.
In conclusion, the use of Erythropoietin can lead to increased sensitivity to sun exposure, as well as changes in the skin’s appearance. It is important to take precautions when going out in the sun to minimize the risk of sun damage and other skin changes. If you experience any skin reactions while using Erythropoietin, it is important to consult with your doctor. By being aware of these potential changes in the skin, you can ensure a safe and effective use of Erythropoietin for the treatment of anemia.
Q&A
1. ¿Qué cambios puede experimentar la piel durante el uso de Eritropoyetina?
Durante el uso de Eritropoyetina, la piel puede experimentar cambios como enrojecimiento, picazón, sequedad, descamación y sensibilidad. También puede haber cambios en la pigmentación de la piel, como manchas oscuras o claras.
2. ¿Estos cambios en la piel son normales durante el tratamiento con Eritropoyetina?
Sí, estos cambios en la piel son normales durante el tratamiento con Eritropoyetina. Sin embargo, es importante informar a su médico si los síntomas son graves o persistentes.
3. ¿Cómo puedo cuidar mi piel durante el uso de Eritropoyetina?
Para cuidar su piel durante el uso de Eritropoyetina, es importante mantenerla hidratada y protegerla del sol con protector solar. También puede ser útil evitar el uso de productos químicos agresivos en la piel y mantener una dieta saludable y equilibrada. Si experimenta síntomas graves o persistentes, consulte a su médico para obtener recomendaciones específicas para su caso.